Ring topology:
In ring topology, each
host device connects to exactly two other devices, creating a circular network
structure. When one host tries to communicate or send message to a host which
is not adjacent to it, the data travels through all intermediate hosts.
Fig. 1: Ring topology.
Advantages of Ring
topology:
· Network
Management: Faulty devices can be removed from the network
without bringing the network down.
· Product
availability: Many hardware and software tools for
network operation and monitoring are available.
· Cost: Twisted
pair cabling is inexpensive and easily available. Therefore, the installation
cost is very low.
·
Reliable: It
is a more reliable network because the communication system is not dependent on
the single host computer.
Disadvantages of Ring
topology:
· Difficult
troubleshooting: It requires specialized test
equipment to determine the cable faults. If any fault occurs in the cable, then
it would disrupt the communication for all the nodes.
· Failure: The
breakdown in one station leads to the failure of the overall network.
· Reconfiguration
difficult: Adding new devices to the network would slow
down the network.
·
Delay: Communication
delay is directly proportional to the number of nodes. Adding new devices
increases the communication delay.
Tree topology:
This topology is the extension
of Star topology and also known as hierarchical topology. In this topology, the
various secondary hubs or devices are connected to the central hub or device
which contains the repeater. In this data flow from top to bottom i.e., from
the central hub or device to secondary and then to the devices or from bottom
to top i.e., devices to the secondary hub and then to the central hub. It
is a multi-point connection and a non-robust topology because if the backbone
fails the topology crashes.
Fig.2: Tree topology.
Advantages of Tree
topology:
Support for broadband
transmission: Tree topology is mainly used to
provide broadband transmission, i.e., signals are sent over long distances
without being attenuated.
Easily expandable: We
can add the new device to the existing network. Therefore, we can say that tree
topology is easily expandable.
Easily manageable: In
tree topology, the whole network is divided into segments known as star
networks which can be easily managed and maintained.
Error detection: Error
detection and error correction are very easy in a tree topology.
Limited failure: The
breakdown in one station does not affect the entire network.
Point-to-point wiring: It
has point-to-point wiring for individual segments.
Disadvantages of Tree
topology:
Difficult
troubleshooting: If any fault occurs in the node,
then it becomes difficult to troubleshoot the problem.
High cost: Devices
required for broadband transmission are very costly.
Failure: A
tree topology mainly relies on main bus cable and failure in main bus cable
will damage the overall network.
Reconfiguration
difficult: If new devices are added, then it becomes
difficult to reconfigure.
Mesh topology:
In mesh topology, a host
device is connected to one or multiple hosts devices. This topology has hosts
in point-to-point connection with every other host or may also have hosts which
are in point-to-point connection to few hosts only.
Fig. 3: Mesh topology.
Advantages of Mesh
topology:
Reliable: The
mesh topology networks are very reliable as if any link breakdown will not
affect the communication between connected computers.
Fast Communication: Communication
is very fast between the nodes.
Easier Reconfiguration: Adding
new devices would not disrupt the communication between other devices.
Disadvantages of Mesh topology:
Cost: A
mesh topology contains a large number of connected devices such as a router and
more transmission media than other topologies.
Management: Mesh
topology networks are very large and very difficult to maintain and manage. If
the network is not monitored carefully, then the communication link failure
goes undetected.
Efficiency: In
this topology, redundant connections are high that reduces the efficiency of
the network.
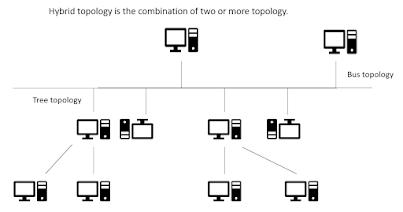
Hybrid topology:
When two or more
different topologies are combined together is termed as hybrid topology. The
combination of various different topologies is known as hybrid topology.
Fig. 4: Hybrid topology.
Advantages of Hybrid
topology:
Reliable: If
a fault occurs in any part of the network will not affect the functioning of
the rest of the network.
Scalable: Size
of the network can be easily expanded by adding new devices without affecting
the functionality of the existing network.
Flexible: This
topology is very flexible as it can be designed according to the requirements
of the organization.
Effective: Hybrid
topology is very effective as it can be designed in such a way that the
strength of the network is maximized and weakness of the network is minimized.
Disadvantages of Hybrid
topology:
Complex design: The
major drawback of the Hybrid topology is the design of the Hybrid network. It
is very difficult to design the architecture of the Hybrid network.
Costly Hub: The
Hubs used in the Hybrid topology are very expensive as these hubs are different
from usual Hubs used in other topologies.
Costly infrastructure: The
infrastructure cost is very high as a hybrid network requires a lot of cabling,
network devices, etc.












0 Comments